Motherboard Components
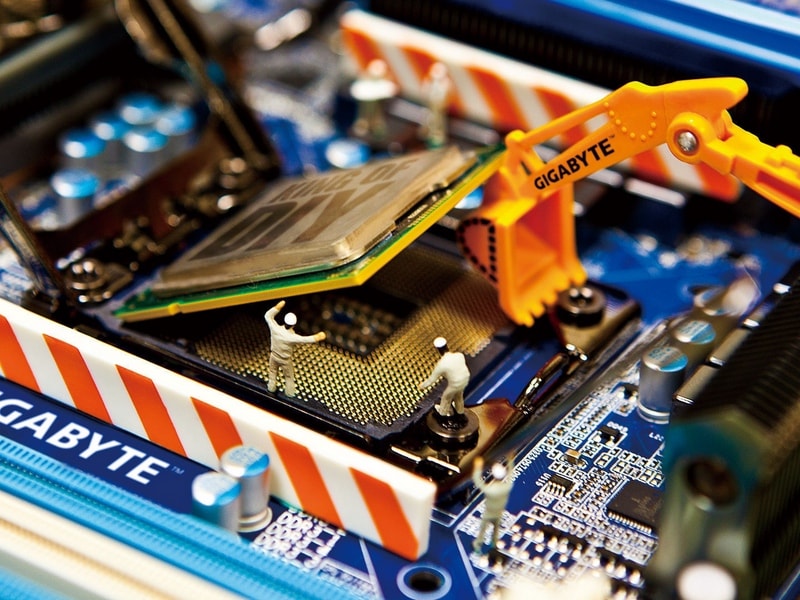
One of the most important elements in a computer is the motherboard, while the other is called the motherboard.
The motherboard design includes the following nodes:
The centerpiece of the entire computer system, although it does not work without the rest of the devices, is the processor. To install it on the motherboard, a special socket socket is used. Sockets have different options for mounting the cooler to cool the processor.
One of the important devices that is located on the motherboard is a BIOS chip. It contains the computer startup program and computer configuration.
When you turn on the computer’s power, BIOS initializes the devices that are connected to the motherboard, checks their performance. If everything is fine, it looks for a bootloader on storage media, such as a “hard” disk, a CD drive, 1.4″ disk drives, which are still found, etc. And the bootloader gives control to the operating system.
The new motherboards can have 2 chips, which increases the stability of the BIOS or BIOS (in English), and is translated as a basic input-output system.
The second most important motherboard device is the chipset.
It is a set of chips that are functionally divided into north and south bridges, which are responsible for the communication of the processor, memory and graphics card, and the communication of slow devices such as a “hard” drive, network card, audio codec, etc. In addition, the North Bridge connects the devices included in the South Bridge and the processor.
The northern and southern bridges are usually made on two microchips, and the northern bridge is supplied with a radiator and often with a cooling cooler for heating during operation. More details about the construction and operation of the northern and southern bridges will be considered later.
The motherboard has sockets or RAM slots, usually next to the processor socket and the northbridge chip.
They contain RAM modules. The number of them can be different: from 2 on cheap boards to 6 on more expensive ones. These RAM slots are connected via buses to the north bridge and through it to the CPU.
Next to the north bridge, perpendicular to the RAM slots, there is a video card slot or slot. In older computers it is usually an AGP connector (translated as a port of a graphic accelerator), and in modern computers it is E – PCI or PCI – Express.
Like the RAM slots, AGP or PCI-E are connected to the north bridge by means of buses, and through it to the central processor.
Near and parallel to the socket AGP or PCI – E on the motherboard there are PCI connectors, which are designed to connect various internal devices, such as sound cards, boards of various FM – and TV – tuners, network cards, internal modems, various controllers of non-standard equipment, allowing the use of computers in many areas of human activity.
PCI appeared earlier than PCI – E and the latter was based on it. They differ, first of all, in bandwidth and performance. At PCI – E it is higher, than at PCI, and it is clear: – first, frequency of work of bus PCI – E is higher than at PCI, and – the second, PCI – E works with devices connected to the northern bridge which possesses the big speed, than the southern bridge and accordingly, the bus PCI connected to the southern bridge.
The actual southern bridge is located on the motherboard next to the RAM connectors and the AGP or PCI-E connector. As it was mentioned above, the southern bridge connects slow devices and with the help of the northern bridge connects the same devices to the processor and RAM.
Usually both northern and southern bridges on the motherboard consist of two separate chips that form a chipset. The chip of the southern bridge is often also cooled by a radiator, especially on new motherboards.
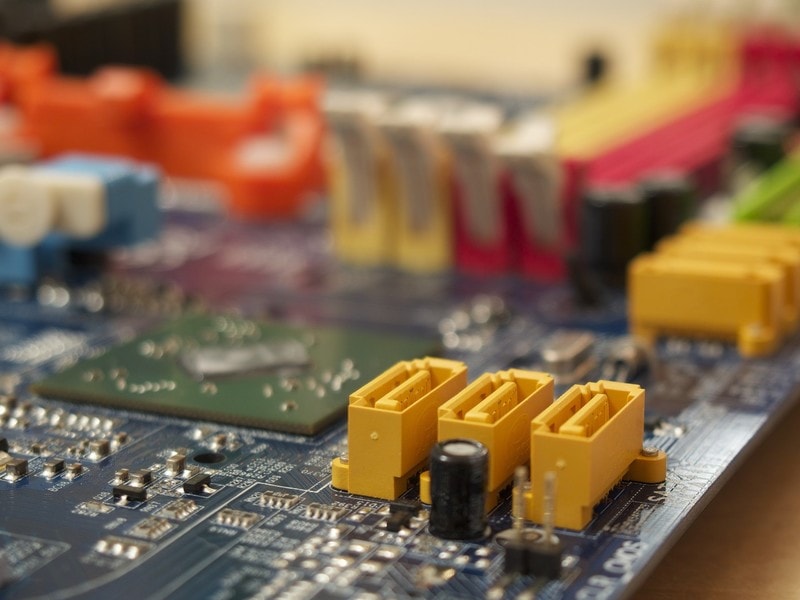
The motherboard has pin connectors for connecting hard drives and optical drives with IDE interface, connectors for connecting hard drives and optical drives with SATA interface.
Nowadays, motherboards have mainly SATA connectors, because IDE are already out of “fashion” and the maximum that can be counted on is the presence of one connector of the IDE interface, unlike SATA – shunters, the number of which can reach 6 (8-10) on the motherboard.
Close to SATA connectors there can be small chips – these are SATA controllers, firms can be different, for example: Promise, Silicon Image, VIA, Marvel.
One of the main tasks of the SATA controller is to create a RAID array of “hard” disks to improve the performance and reliability of data storage on the disks.
On the motherboard there is a BIOS battery, which serves to permanently power the BIOS chip, which stores the boot program and the configuration of the computer.
The motherboard may have connectors for additional USB ports, which may be located on the front panel of the CPU Box, for example.
On the motherboard there is a pin connector for connecting the buttons of the front panel of the system unit: power on, reboot, indicators of the “hard” drive and power on, connection of the speaker.

